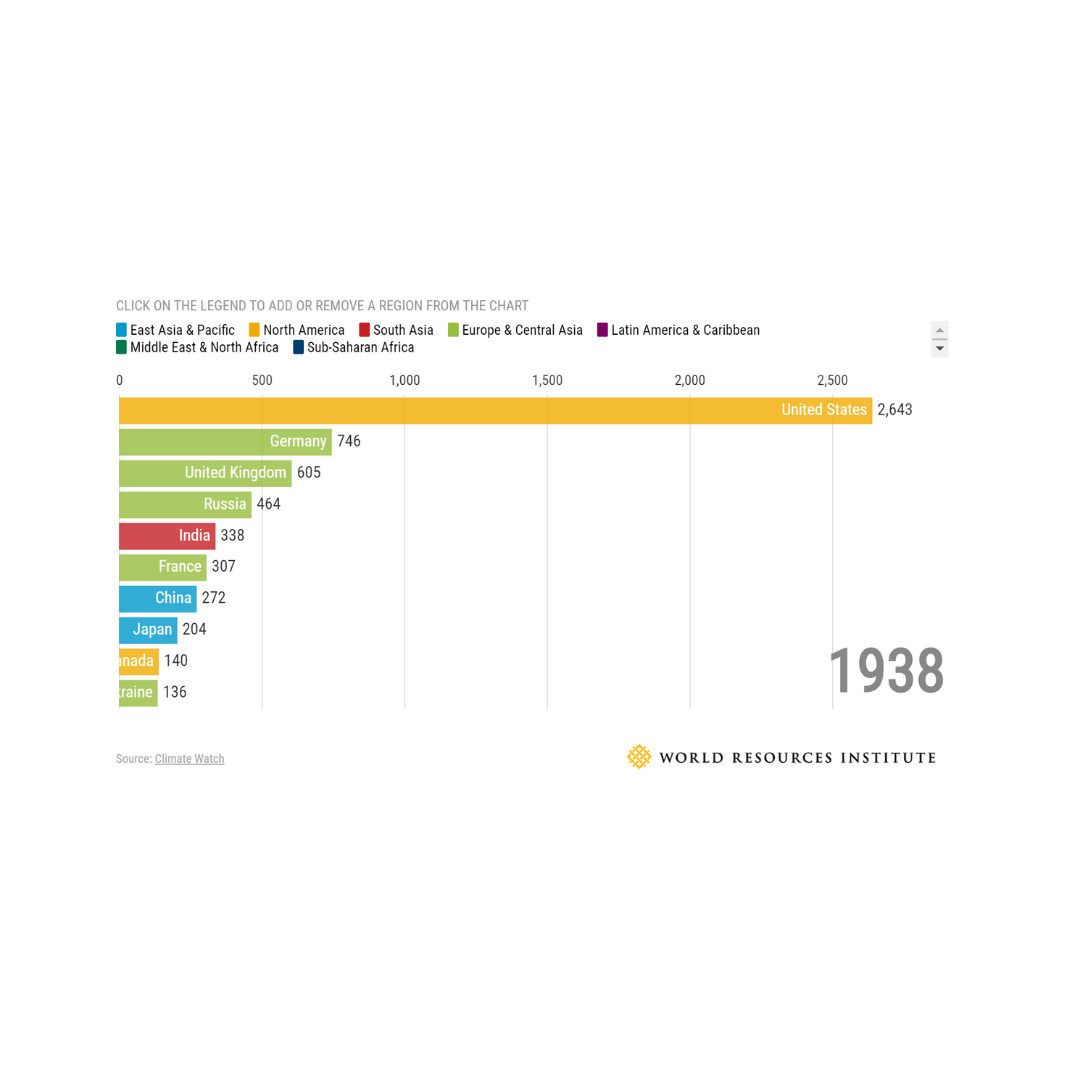
You’ve seen the memes (even we couldn’t help ourselves at the top of this post): as industries slow, people fly less, and emissions fall. There’s truth that lower economic activity can mean lower emissions (especially when people aren’t allowed out of their house to commute an hour to work), but unless we get serious about actually restructuring our society to be more sustainable, history shows emissions will bounce right back – check out the Great Depression in the 1930s and the end of World War II in 1945 below.
So worth considering if you can keep working from home after this Pandemic passes, and other ways you can lower your emissions.
If you’ve been on social media these last few weeks you’ve probably seen the fun, lighthearted stories about the return of nature to our cities in the sudden absence of human activity. Posts about swans and dolphins returning to the suddenly crystal clear waters of Venice, or elephants stealing corn wine and getting drunk while the humans were out social distancing have both been debunked as either completely fabricated for the likes (Venice Dolphins), or are already part of day-to-day life and nothing out of the ordinary (although elephants stealing corn and getting drunk is still funny).
What is real news is that 2019 saw the biggest fall of global carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the power sector at 2%! Thanks to reduced coal usage in Europe (down 24% with a drive towards renewables 🙌🏼) and the U.S. (down 16% because natural gas became cheaper 🤦🏼). Oh– and China’s output rose so they’re now responsible for half of the global coal-fired power generation. Here’s the thing: the world needs to drop coal usage by 11% every year to keep within a warming limit of 1.5 degrees Celsius, and natural gas may not be as dirty of a fuel as coal, but it’s nowhere near carbon neutral. [The Guardian]
About The Author

Swarnav has over 10 years of experience in the energy & climate tech space, holds 2 patents and is active in the tech, climate and media industries. He specializes in Product/Product Innovation as well as Go-To-Market and Growth Strategy.
By training he’s a Materials Engineer with a background in research from his time at Georgia Tech and University of Illinois (UIUC).
He founded TouchLight a utility backed energy company focused on developing IP for utilities and startups pushing electrification forward. He also serves as the appointed Chairman for the Town of Yorktown’s Climate Smart Communities Task Force, where he helps with drafting legislation and enabling sustainability efforts within the town.
Concurrently, Swarnav founded The Impact to help investors, emerging founders and driven climate enthusiasts discover and identify new climate-tech startups, technologies and opportunities before they hit the traditional media sources.